Annuity Basics
Annuities are considered the opposite of life insurance. Instead of dying too soon, you live too long. An annuity is about making sure you have money to last you while your alive, especially if you’re retired and not bringing in income.
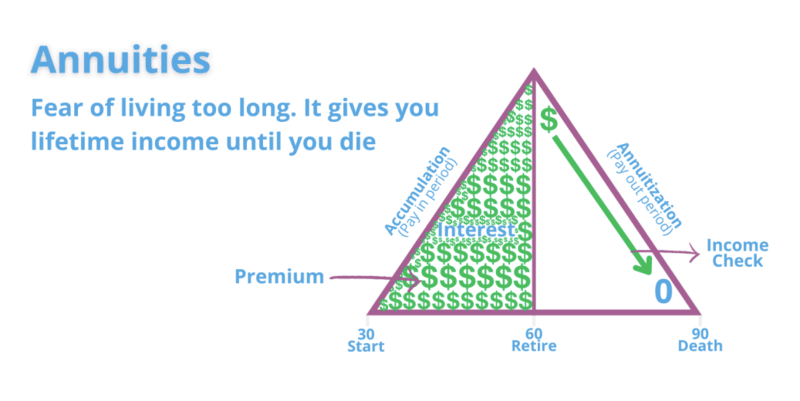
Most of us are familiar with a 401k, and that is an annuity. You’re saving money NOW, so you can have it LATER. That’s the whole premise of an annuity. Save now, spend later.
The most important thing to know about an annuity for the test are the definitions.
When you put money in, that is called Accumulation or the pay in period.
When you switch from putting money in to taking it out, you called that Annuitization.
When you’re taking the money out, it’s called the Annuity Period or Pay Out Period.
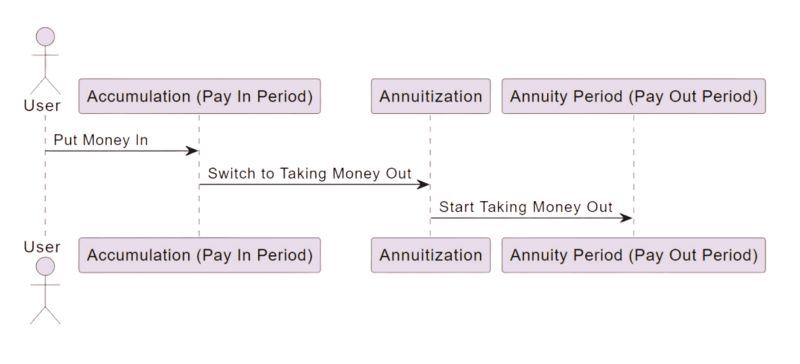
When you take years to put money into it, it’s called a Periodic Premium Annuity.
When you put the money in all at once, like winning the lottery and you want to prevent spending it all right away, it’s called a Single Premium Annuity.
If the time between the first pay in to the first payout is less than a year, it’s an Immediate Annuity.
If the time between the first pay in to the first payout is more than a year, it’s a Deferred Annuity.
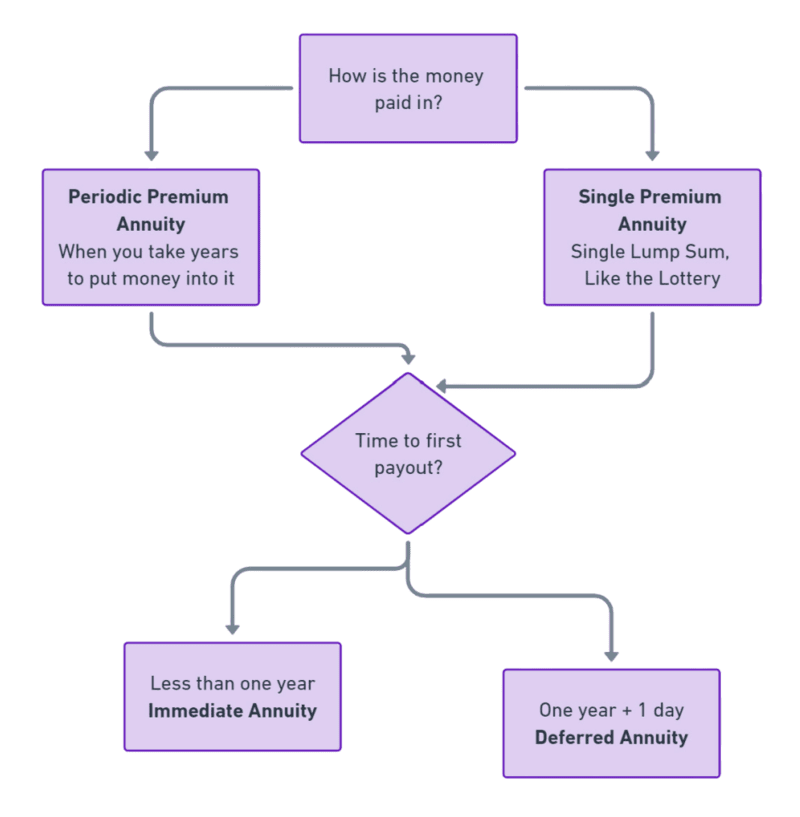
After annuitizing, aka, you enter the payout period, there are a few options.
- Life Income Annuity
- Fixed Period Certain
- Fixed Amount Certain
Life Income – This type of payout is the original idea of an annuity. If you are going to live beyond your money, an annuity is meant to protect you from that. If you fill your annuity with money, annuitize it, and begin taking it out you could possibly live beyond the money that is in the annuity. If we left it at that, an annuity would not be serving its purpose. Therefore, the life income annuity will continue to pay you for the rest of your life, even if the annuity is drained of its funds. This sounds like a really great idea, however there is some risk involved. Because the insurance company is willing to pay you even after your money has run out, they will also say that if you die before the money runs out, that they can keep it. This is why there is no beneficiary on a life income annuity. If the annuitant dies any money left over will become the company’s money. You would have to consider if this is a fair trade-off. If you really think that you’re going to live beyond the money in the annuity, if you think that you’re healthy enough to live that long, this might be a great option for you. If you’re not convinced that you will live past the money in your annuity, this would be a bad idea because you and your heirs would lose any money in that annuity when you die. Some people really hated the idea of dying and losing all that money to the company. This is why they created fixed period certain or fixed amount certain.
Fixed Period Certain – This payout will guarantee that money will pay out for at least a certain number of years, even if the annuitant dies, before the company is allowed to keep the rest of the money. So, if you annuitize, and you died in the first year in but you had a 10-year certain, the annuity will continue to pay out for at least the next nine years to whoever you’ve selected as a beneficiary. This is a way of making sure that at least a good chunk of your money goes towards your family instead of going towards the company while also making sure that you have a life income.
Fixed Amount Certain – This payout works the same way as fixed period certain, except instead of focusing on the amount of time, you focus on the amount of money. So if the annuitant dies before these certain amount has been paid out to the annuitant, the rest of that amount will be paid out to a beneficiary before the company is allowed to keep the rest.
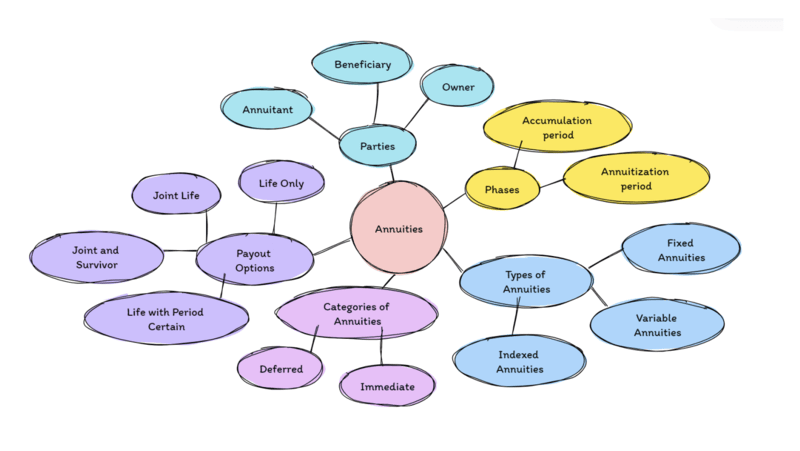
Annuities Recap:
There are 2 Phases:
- Accumulation Period – when you are making payments into the annuity
- Annuitization Period – when payments come out, to insured Parties
There are 3 parties involved although the Owner and the Annuitant are often the same person:
- Annuitant – the Insured person; policy issued on annuitant’s life
- Beneficiary – will receive any amount contributed to annuity (plus any gain) if annuitant dies during accumulation period
- Owner – has all rights to policy (usually annuitant); can be corporation or trust
There are 3 broad Types of Annuities
- Fixed Annuities:
- Guaranteed
- Fixed Payment Amount
- Premiums in their general account
- Variable Annuities – payment not guaranteed; premiums are in separate account, and invested in stocks and bonds … I tell students when they see the V in Variable the 2 lines that form the V should remind them that… an agent must have BOTH an Insurance license AND a securities license to sell these. Also these are regulated by BOTH the State Insurance Department AND the Federal govt because of the securities involved.
- Indexed Annuities – interest rate tied to an index; earn higher rate than fixed annuities, not as risky as variable annuities or mutual funds ….. Only need an Insurance license to sell these.
Categories of Annuities
- Immediate – purchased with a single premium. Income payments start within one year from the date of purchase.
- Deferred – purchased with either lump sum or periodic payments premium. Benefits start sometime after one year from the date of purchase (often used to accumulate funds for retirement).
Common Payout Options:
- Life Only – insured cannot outlive income. Any monies not paid out are retained by company at insured’s death. Pays highest monthly amount.
- Joint Life – 2 or more annuitants receive payments until first death, then payments cease.
- Joint & Survivor – income for 2 or more that cannot be outlived. Often used with period certain. When one annuitant dies, the other receives either 1/2 or 2/3 of the original payment amount.
- Life with Period Certain – specific monthly payment for life and a specific period of time (e.g. Life plus 10-year certain). If annuitant dies before payment period is up, payment goes to beneficiary.
Recommended: Gold
The GOLD Course is ALWAYS the recommended class series for all students as it teaches the material in more depth. Over 30 hours of the most in depth classes with a more intensive teaching of the topic. Learn more about L&H GOLD
Share the Post
Click to share the post to your network





