Elements of a Legal Contract
Agreement – Offer and Acceptance (Offer = Customer submits and application, Acceptance = insurer issues policy).
Consideration – Both parties bring something of value (Customer brings premium and application, Insurer bring a promise to pay a claim).
Competent Parties – Not under the influence of drugs or alcohol, sound mind, legal age.
Legal Purpose – Cannot be against public policy.
Insurable Interest – Required to be proven at time of policy being issued. Must have blood, business or money to buy a policy on someone.
Representation – Statements that are believed to be true but are not guaranteed to be true.
Warranty – Absolutely true statements.
Misrepresentation – Untrue statements.
Material Misrepresentation – Info that would have changed the insurers decision had they known.
Adhesion – Insurer write the policy, customer either takes it or leaves it.
Aleatory – Unequal Exchange (customer pays small monthly premium, insurer pays very large claim).
Unilateral – One sided promise, only the insurer are legally bound to do anything.
Conditional – Both parties have rules/duties they must follow/do.

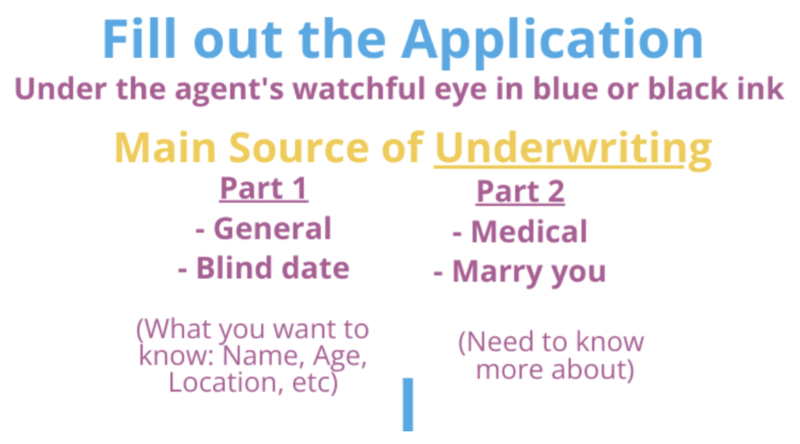
Completing the Application
Entire Contract – Copy of Application stapled to the Policy.
Application – Filled out by the agent/customer, main source of underwriting information.
- Application + Policy stapled together is called and Entire Contract
- Notice to the Applicant if credit reports will be pulled
- Agent is responsible to ensure its complete and accurate
- Changes (best to start over, if not, draw a line through error and customer initial)
- Signatures (Agent, Owner and Insured) (Owner and Insured can be the same person)
Premiums with the Application – (If paid with the application, it’s conditional and will be issued at the date of application, so long as everything checks out).
APS (Attending Physicians Statement) – Filled out with all past medical history and treatments.
MIB (Medical Information Bureau) – Group of insurance companies who share past medical history from prior applications to make sure the customer is not lying. Cannot be the sole reason for declining coverage.
Medical Exam – Done by a professional, paid for by the insurance company.
Fair Credit Reporting Act – Protects the consumer against the circulation of inaccurate of obsolete personal financial.
Investigative Consumer Reports – Interview friends/family for lifestyle and character.
HIPPA – Protects the privacy of a persons health information.
Free Look/Right to Examine – Upon delivery time to look over a policy and if returned will get all their money back (10 days on most all policies, 30 days on Medicare Supplement and Long Term Care).
Replacement – Selling a new policy when someone already has one.
- Do not cancel the old one until the new one is issued
- Consider that certain conditions maybe covered on the old policy but excluded on the new one
For more detailed Study Notes about Completing the Application Click Here.
Types of Health Policies
Basic Medical – Low $ limits, first dollar coverage, not good for catastrophic medical expenses.
Major Medical Insurance – Covers catastrophic expenses by using copays/deductibles/co-insurance.
- Deductibles – paid up front by the insured, the higher it is, the cheaper the premium (flat $ amount)
- Co-insurance – Cost sharing between the insured and the insurance company after the deductible is paid (%)
- Co-pay – Set dollar amount the insured pays up front for any services
Stop Loss – The max out of pocket an insured will pay, and then insurance covers all the rest.
Maximum Benefits – max a person can collect in their lifetime, usually in the millions.
Exclusions – War, self inflicted, dental/hearing/vision/custodial care, elective cosmetic surgery, workers comp injuries.
HMO – A group of docs and hospitals who offered medical care on a pre-paid basis, focusing on prevention and low costs.
- Directly provides services, its not an insurance company, it finances and care to the subscribers
Gatekeeper/Primary Care Physician – Regular doc who must refer you if you want a specialist, saves money.
Preferred Provider Organizations (PPO) – Ins company that makes deals with doctors to offer lower costs.
- In-Network – Docs who made deals to charge lower cost, PPO will pay more of the cost
- Out-Of-Network – Docs who haven’t made deals to lower costs, PPO will pay less of the cost
No Gatekeeper, no referrals needed.
FSA (Flexible Spending Account) – (cafeteria plan) – Pre-tax money set aside for medical expenses in that year, no roll over.
- NO IRS limit for the FSA, but an employer usually sets one
- Dependent Care FSA does have an IRS limit, can only be used on true dependents
- Limits are selected each year and can only be changed if a major life event occurs
HSA (Health Savings Accounts) – Monies from employers and employees for those who chose a High Deductible Plan.
Tax Deductible – Can roll the money over, only for medical costs (if not, 20% penalty plus taxed*if Medicare age, no penalty, just tax).
Disability Income Insurance – Replaces lost income in the event of a disability that prevents the insured from working.
Elimination Period – Deductible in days, time the insured must be disabled and out of work before benefits are paid out.
Benefit Period – Length of time the insurer is responsible to pay for each disability.
- The longer the Elimination Period, the lower the premium
- The longer the Benefit Period, the higher the premium
Presumptive Disability – Automatically disabled at the loss of any two limbs, speech, hearing, total blindness.
Social Insurance Supplement (SIS) – Rider pays during the waiting period, and any amount after is SS isn’t enough.
Business Overheard Expense – If the small biz owner is disabled, this will pay his rent and employees salary, but NOT their own income. (Premium is paid by the biz, can be tax deducted, thus benefits are taxed when paid out).
Disability Buy Sell – Biz partners buy policies on each other to buy out the others share of the biz if disabled.
Reducing Term – Pays loans a biz owner has if they become disabled.
Key Person – Purchased on the life of a key employee who would be expensive to replace (biz pays the premium, biz owns the policy, biz gets the benefit, cannot be tax deducted, benefits are tax free).
Accidental Death and Dismemberment – Rider or separate policy.
Principal Sum – Full amount paid for death, accidental loss of two limbs and /or full eyesight.
Capital Sum – % paid for dismemberment (one limb, one eye).
Long-term Care – Money to pay for services that a individually can no longer do independently.
- Eligible for benefits – Cannot preform Activities of daily living (what do you do for a baby)
- Elimination Period is 30 days of being confined to a nursing home
- Benefits are paid listed as a set $ limit a day, the minimum benefit length is 12 months
Group Policy – Contract is between the insurance company and the group sponsor (employer, association etc).
Group Contract – One policy is issued called the Master Poilcy, only sent to the group sponsor.
Associations – Can buy group insurance if they have 100+ members, active for 2+ years, and have annual meetings. They can be either contributory or non contributory.
Polices – Can either be purchased as an individual or within a group.
Individual – Is more expense, underwriting is more intense, based on medical history/occupation.
Group – Is easy underwriting, and subject to revaluation each year, Master Policy.
Continuation of Coverage Under COBRA (Consolidated Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act of 1985)
- Allows employees to stay covered in the group, even though they left the group
- Any employer who has at least 20 employees must extend group coverage to terminated employees due to:
- Voluntary termination of employment (quitting)
- Termination of employment (unless it’s for gross misconduct (sexual harassment) like downsizing
- Employment Status Change (full time to part time)
- Dependent (spouse, child 0-26yrs) of an employee from either death or divorce, or one of the above
Must decide within 60 days of leaving the group if they want to have COBRA Coverage is extended for 18 months for the individual, 36 months for Dependents
Premium is now paid solely by the individual/dependent and it’s 102% of the premium.
Disqualifying Events – Under Cobra, nonpayment, get new coverage, eligible for Medicare, employer end the whole policy.
Accident Only – Covers only accidents.
Specified/Dread Disease – (Cancer, heart, paid as a fixed dollar upon diagnosis/hospital confinement).
Critical Illness – (Similar to Dread Disease, must live for a certain time after diagnosis to be paid).
Hospital Indemnity – Daily/weekly/monthly set dollar amount to pay if confined to a hospital.
Vision/Hearing – (Per ACA pediatric vision and dental are required).
Policy Provisions, Clauses and Riders (25%)
Uniform Individual Accident and Sickness Policy Provisions Law – Standard provisions must be included in all health policies. Can be reworded by an insurer to long as it does not make the provision less favorable to the insured.
Mandatory Provisions that must be included in all Health Policies
Entire Contract – Copy of Application stapled to the Policy.
Grace Period – Coverage is still in force but the premium hasn’t be paid. If a claim occurs during the time, the claim will pay out in full minus the missed payment.
Reinstatement – Time after a policy cancelled due to non-payment and the customer wants to get it back by paying all missed premium, there is a 10 day probation on sickness after reinstatement.
Change of Beneficiary – Can be changed anytime by insured, unless irrevocable, then beneficiary must give permission.
Claim Procedures
Notice of Claim – Insured tells insurer of claim within 20 days/reasonable.
Claims Form – Must be sent to insured after notice of claim, usually 15 days.
Proof of Loss – Insured submits this within 90 days from the date of incident/sickness.
Time Payment of Claims – Tells insurer how quickly to pay a claim, usually immediately.
Payment of Claims – Tells insurer who to pay to, could be doctor or insured directly.
Physical Exams and Autopsy – Insurer has the right to these.
Time Limit on Certain Defenses – Similar to incontestability in life/cannot deny a claim after 2 years, unless fraud.
Legal Action – For insured to sue, must wait 60 days, but no more than 3 years.
Misstatement of Age – Benefits are adjusted up or down to match correct age.
Change of Occupation – Insured must tell the insurer, benefits/coverages maybe adjusted.
Illegal Occupation – If insured is injured while committing a crime, no coverage.
Other Provisions and Clauses
Insuring Clause – Statement that this insurer is covering this insured for these perils.
Free Look/Right to Examine – Upon delivery time to look over a policy and if returned will get all their money back (10 days on most all policies, 30 days on Medicare Supplement and Long Term Care).
Consideration Clause – Both bring something of value (Insured = premium + app, Insurer = promise to pay).
Elimination Period – Deductible in days, time the insured must be disabled and out of work before benefits are paid out.
Wavier of Premium – While the insured is disabled, the premium is waved after the elimination period, and any premium paid during that time will be refunded.
Deductibles – Paid up front by the insured, the higher it is, the cheaper the premium (flat $ amount).
Co-insurance – Cost sharing between the insured and the insurance company after the deductible is paid (%).
Co-pay – Set dollar amount the insured pays up front for any services.
Usual/Reasonable/Customary – Price is averaged based on what docs in that geographic region are charging.
Future Increase Option (FIO) – Rider/Guaranteed Insurability Rider- more coverage at various intervals without proving insurability.
Renewability Clause – States under what conditions a policy can be renewed.
- Noncancellable – Can’t be cancel, premium cannot increase, renewed until 65
- Guaranteed Renewable – Renewable till 65, premium increase on a class basis only
- Non-renewable (cancellable term) – only for short term medical
Social Insurance
Medicare Parts:
- Part A – Hospital care, inpatient care in a skilled nursing facility, home health care and hospice care.
- Paid for by taxes, most people have free part A. If you fail to sign up when you are first eligible, 10% penalty
- Part B – Medical Insurance, doctors services and other medical services.
- Paid for with taxes and a standard premium
- Part C – Medicare Advantage, allows Medicare participants to have an HMO or PPO.
- Paid for with premiums, usually costing no more than the standard premium
- Part D – Prescription Drug Benefit
- Paid for with Premiums
Eligibility – 65 or older, end-stage renal disease/kidney failure, or have been collecting Social Security disability for 2 years.
- If you’re eligible for Medicare, you cannot get a ACA policy from the market place
Enrollment – Initial (3 months before and after turning 65) General (Jan 1st-March 31st) Special (as needed).
- If you are covered under another group plan, Medicare is considered secondary
Part A – Must sign up when 1st eligible or there is a 10% penalty when you eventually sign up (unless you’re special).
Exclusions – Intermediate nursing home care, custodial care, dental (unless accident), war.
Part B – When you enroll in A, B is automatic unless you decline it (does not cover drugs, expect when in a hospital or when the drugs need durable medical equipment like a infusion pump or nebulizer).
- 80/20 Co-insurance and No Max out of Pocket limit
Part C – Medicare Advantage, works just like an HMO or PPO – You MUST be enrolled in Part A and B to get C.
Part D – Drugs, Donut Hole.
Words to Know
Limiting Coverage – Max amount a doc can charge a Medicare patient for a covered service.
Durable Medical Equipment – Oxygen equipment, wheelchairs, nebulizer, infusion pump, medically necessary stuff.
Medicare Supplement/Medigap – Sold by private insurance companies to fill in the gaps of Medicare.
- The OBRA Act said anyone who sells them must use the same language/same plans
- The only thing allowed to be different is the premium
- Must have Part A and B in order to purchase these plans, open enrollment is 6 months after getting Medicare
- Medicare Supplement cannot duplicate Medicare Coverage
- Guaranteed Renewable, 30 day free look period
Plan A – Core Plan, and any other plan must include these benefits.
- Any company who sells Medicare must sell Plan A. After that they can offer any of the other plans as they wish
Medicare Select – In exchange for a reduce premium, the insured agrees to go to select providers.
Medicaid – Fed and State Program for those who are below the Federal Poverty Level.
Social Security Disability – Old Age Survivor Insurance- Federal insurance for the elderly or disabled.
Qualifications – You must pay into the system to take from the system, aka, you must work at a job.
- Fully Insured – Worked 40 quarters (10 years)
- Currently Insured – Worked 6 credits within the last 13 quarters (1.5 years in the last 3 years)
Definition of Disability – Expected to last over 12 months or result in early death.
Waiting Period – Five months of being disabled before getting any benefits.
Disability Income Benefits – Based on PIA (primary insurance amount).
Other Health Insurance Concepts (5%)
Dependents – Age 26 (natural child, step or adopted, unmarried) or older but incapable of self care.
Coordination of Benefits – If there are two policies on one person, they will coordinate benefits to prevent over insurance.
- Primary – the plan you get from your employer, pays all of its coverage first, then submits to secondary
- Secondary – the plan your covered on by your spouse’s employer, pays up to their duties after primary paid
*In no case will both plans ever pay more than what the actual medical bill is*
Dependents can be on both plans and will either be primary on their parent’s plan following the Bday rule or gender rule
- Birthday Rule – Whichever parent’s birthday happens first during the year is primary
- Gender Rule – The father is always primary (or if divorced, whomever has custody is primary)
Occupational Vs. Nonoccupational Coverage
Occupational – Will cover a person either on or off the job.
Non-Occupational – Will only cover a person who is not working at the time of injury (your job should have workers comp).
Total Disability Plan – Protects the family if the wage earner becomes disabled.
Partial Disability – Can’t work at all your normal hours due to disability, get paid for half of the missed hours.
Residual Disability – Can’t work all your hours due to disability and you get paid for all the missed hours.
Managed Care – Control the behavior of the insureds to save money.
Workers Compensation – Work related injury or sickness- comes from your employer.
- Provides Medical, income, death and Rehabilitation benefits
Subrogation – Insurers right to seek recovery of damages from the responsible third party.
PPACA (Patient Protection and the Affordable Care Act) “Obama Care”.
- Eligibility – US Citizen/lawfully present, live in the US, not in jail, not on Medicare
Premium Rates – Based on family size, geographic region, age, tobacco use.
Essential Benefits – Must be offered on all plans, or else there is a fine to the employer or individual.
Guaranteed Issue/Renewability – Plans must be offered to anyone who enrolls and always renewed.
Dependents – Can be covered until age 26.
Emergency Care – Must be covered in and out of network.
Pediatric Vision and Dental – Are required within the medical plans.
Metal Tiers – Co-insurance amounts Bronze 60/50, Silver 70/30, Gold 80/20, Platinum 90/10.
Newborns – Covered immediately, the moment of birth(if premium increase notify the insurer in 31 days).
Taxes
Simple Statements:
Employers can tax deduct premiums, employees cannot.
If an employer pays the premium, the benefits will get taxed (EXCEPT MEDICAL).
If the employee pays the premium, the benefits will NOT be taxed.
If employer and employee share the premium, the benefit portion from the employee is tax free, the benefit portion from the employer is taxed.
Key Person can not be tax deducted, thus the benefits will NOT be taxed.
Group Medical/Health are the only premiums that can be taxed deducted and benefits received tax free.
Tax Deduct = write off = no taxes are paid
Bigger Statements:
Health/Medical has tax benefits all around, it’s the exception to all the rules below, employers can tax deduct the premiums, and employees get the benefits tax free. All other policies like disability will be taxed either via the money used to pay for the premium or the benefits received will be taxed.
Employers can tax deduct any premiums they pay except for Key Person (on KP, benefits are tax free).
Employees are not able to tax deduct any premiums THEY pay, thus the benefits are tax free.
Recommended: Gold
The GOLD Course is ALWAYS the recommended class series for all students as it teaches the material in more depth. Over 30 hours of the most in depth classes with a more intensive teaching of the topic. Learn more about L&H GOLD
Share the Post
Click to share the post to your network





